Insider Threats: Who Is at Risk?

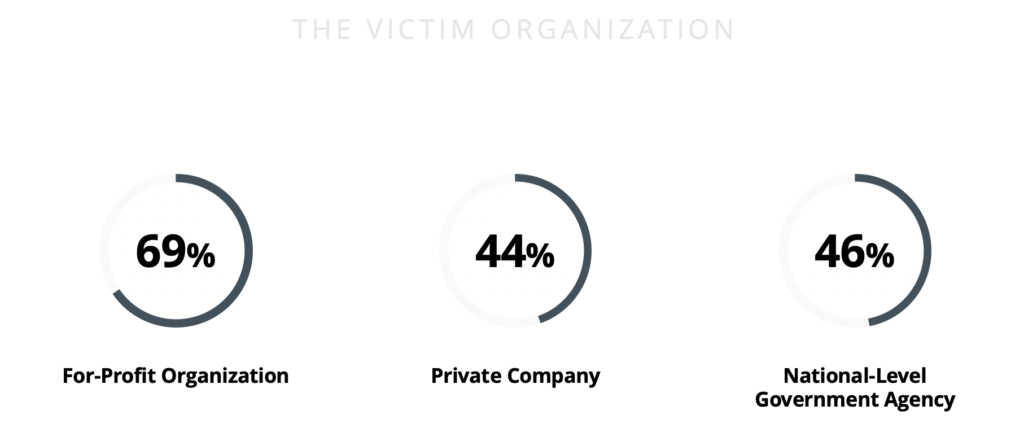
According to recent Occupational Fraud 2022: A Report to the Nations by ACFE, the portrait of most-probably-victim looks the following: It’s a for-profit private company or a government organization with internal control weaknesses that contribute to the fraud.
More than two-thirds (69%) of frauds, as per report, occurred in for-profit organizations. Nonprofit organizations were the victims in only 9% of the reported fraud cases. 44% of the victim organizations are private companies with a median loss of USD 120,000 and 25% are public companies with USD 118,000 accordingly.National-level government agencies represented the highest number of reported frauds in their category (46%) and had the greatest median loss of USD 200,000, which is nearly four times the median loss incurred by state/provincial level entities (USD 56,000). Local governments suffered the second-highest median loss of USD 125,000 more than twice as much as state/provincial-level entities.
Corruption as a main threat
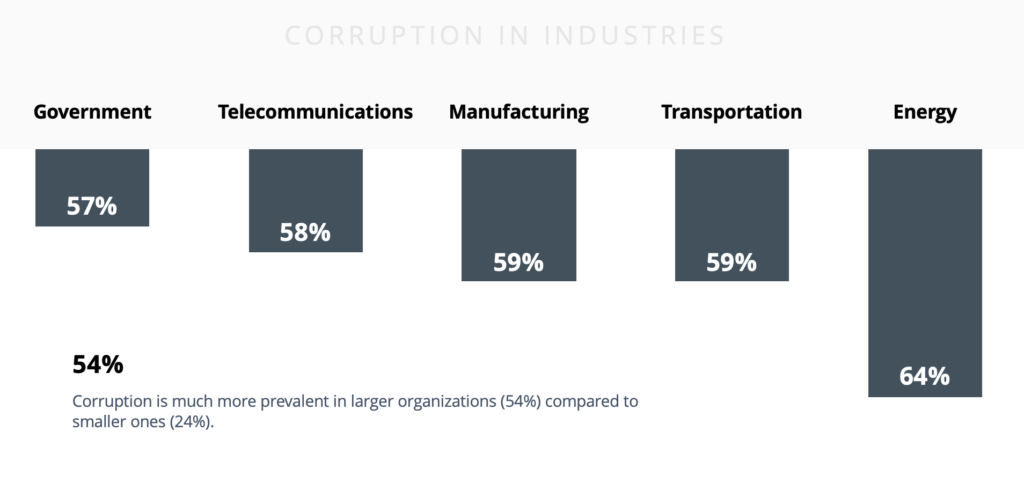
Industries, that obtain and store more sensitive data, such as Financial or Healthcare organizations, are perceived to be primarily at risk and fall under heavy fines and reputational damage. But the study showed that the main insider threat in every researched industry is corruption, making the risk level independent on data volume. 64% of all relevant cases in Energy are associated with corruption, 59% - in Manufacturing, and Transportation and warehousing, 58% - Telecommunications, 57% - Government, etc. Corruption is much more prevalent in larger organizations (54%) compared to smaller ones (24%).
Big problem for a small organization
Although corruption hits larger organizations more, small businesses (<100 employees) had the highest median loss of USD 150,000. While the largest organizations (more than 10,000 employees) had a median loss of USD 138,000. Even though the median loss figures for small and large organizations were similar, the impact of such a loss is likely far more significant at a smaller organization.
Preventive measures
Nearly half of cases in the report occurred due to lack of internal controls (29%). The presence of anti-fraud controls led to lower fraud losses and quicker fraud detection. Majority of victim organizations modified their anti-fraud controls following the fraud.
Popular posts

One of the Largest Technical and Vocational Education and Training Service Providers in South Africa Uses Zecurion Next Generation DLP

One of the Largest World’s Upscale Hospitality Brands Protects Its Business in Turkey with Zecurion
Subscribe to our blog updates
You will receive only really useful emails and will always be able to unsubscribe from this mailing if, suddenly, your interests change
